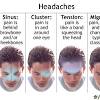
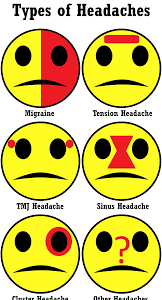
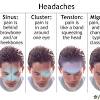
What time of year are migraines most common? January, February, July, August, fall, and spring are common. Headaches around the same time of day or night. They tend to peak from 1 to 2 a.m., 1 to 3 p.m., and 9 p.m., Grosberg says, but attacks can happen at any time.
How do you treat weather migraines? The medications used to treat weather-related migraines are the same as those used to treat other migraine headaches, with the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs like ibuprofen, naproxen and others) and the triptans (sumatriptan and others) being the most important medications.
Why do I get migraines when the weather changes? For some people, weather changes may cause imbalances in brain chemicals, including serotonin, which can prompt a migraine. Weather-related triggers also may worsen a headache caused by other triggers. If you feel your migraines are triggered by weather, you may be understandably frustrated.
How do you stop a barometric pressure headache?
Can you prevent a barometric pressure headache?
- Stay hydrated.
- Document and avoid food triggers.
- Get a solid eight hours of sleep every night.
- Try to keep your stress under control with meditation.
- Exercise on a regular basis.
- Eat a well-balanced diet full of fruits and vegetables.
What time of year are migraines most common? – Additional Questions
How long do barometric pressure headaches last?
headaches that can last between 4 hours and 3 days. sensitivity to light, sounds, and smells. nausea, abdominal pain, and vomiting. distorted vision.
Can barometric pressure cause a migraine?
Weather changes almost inevitably cause variations in atmospheric pressure, which can increase the likelihood of headache and migraine. A 2017 study demonstrated a positive association between the atmospheric pressure and the amount of migraine pain a person experiences.
Does high or low barometric pressure cause migraines?
Specifically, we found that the range from 1003 to <1007 hPa, i.e., 6–10 hPa below standard atmospheric pressure, was most likely to induce migraine.
Why do I get migraines when it rains?
If you’re prone to getting headaches, you could find that grey skies, high humidity, rising temperatures and storms can all bring on head pain. Pressure changes that cause weather changes are thought to trigger chemical and electrical changes in the brain. This irritates nerves, leading to a headache.
What does a high pressure headache feel like?
a constant throbbing headache which may be worse in the morning, or when coughing or straining; it may improve when standing up. temporary loss of vision – your vision may become dark or “greyed out” for a few seconds at a time; this can be triggered by coughing, sneezing or bending down. feeling and being sick.
Does drinking Gatorade help with headaches?
Hydration
Dehydration can contribute to a headache, but it can be easily avoided. Grabbing a good old-fashioned glass of water can help as much as an electrolyte-containing beverage such as Pedialyte, Gatorade, or Powerade.
Can lack of potassium cause migraines?
Defective potassium channels involved in pain detection can increase the chance of developing a headache and could be implicated in migraines, according to research in mice published in eNeuro.
Can low sodium cause migraines?
Migraines could be triggered by dehydration and sodium or salt deficits. Although this is not a theory that has been tested yet, consider the first treatment a migraineur receives in the ER – IV fluids with electrolytes.
How does magnesium help with migraines?
Some scientists believe that magnesium blocks signals in the brain that lead to migraines with an aura, or changes in vision and other senses. Research also suggests that magnesium stops certain chemicals that cause pain.
What is a cocktail for migraine?
A migraine cocktail is a combination of medications that’s given to treat severe migraine symptoms. The exact medications used in a migraine cocktail can vary, but it typically includes triptans, NSAIDs, and antiemetics. A migraine cocktail is also available in OTC medication.
Does B12 help with migraines?
According to a 2020 study, headaches were the most common symptom of vitamin B12 deficiency in adolescence. Other research shows that vitamin B12 might help treat chronic migraine. In a 2019 study of 140 people, researchers found that the participants who had migraine also had low blood levels of B12.
What vitamin deficiency causes headaches?
Vitamin B2 Deficiency
The B vitamins help to protect from headaches, according to the National Headache Foundation, but it is B2 (riboflavin) that really stands out and where a deficiency may lead to headaches.
Can low iron cause migraines?
A deficiency of iron or vitamins can lead to headaches related to low oxygen levels in the brain. IDA has also been shown to play a role in migraine, especially during menstruation.
Can a B12 deficiency cause headaches?
B12 deficiency can cause a variety of symptoms, including fatigue, headaches, depression, pale or yellow skin, mental impairment, and pain and inflammation in the mouth and tongue. Many of the symptoms caused by low B12 levels are not specific to B12 deficiency, which can cause the condition to go undetected.
Can low magnesium cause headaches?
Symptoms of low magnesium include fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, muscle cramping, tingling, and muscle contractions. Low magnesium is also linked to headaches and migraines. It’s estimated that many people don’t get enough magnesium through their diets.
How can I tell if my magnesium levels are low?
Signs of a magnesium deficiency
- Loss of appetite. This is generally the first sign of hypomagnesemia.
- Nausea or vomiting. Another of the nonspecific magnesium deficiency symptoms is nausea or vomiting.
- Fatigue.
- Weakness.
- Muscle spasms and cramps.
- High blood pressure.
- Irregular heartbeat.
- Seizures.
How do I know if Im short of magnesium?
Magnesium deficiency is diagnosed via a blood test and sometimes a urine test. Your doctor may order the blood test if you have symptoms such as weakness, irritability, abnormal heart rhythm, nausea and/or diarrhoea, or if you have abnormal calcium or potassium levels.