What is the best medicine for chronic migraines? Triptans. Prescription drugs such as sumatriptan (Imitrex, Tosymra) and rizatriptan (Maxalt, Maxalt-MLT) are used to treat migraine because they block pain pathways in the brain. Taken as pills, shots or nasal sprays, they can relieve many symptoms of migraine.
How do you fix chronic migraines? Options include topiramate (Topamax, Qudexy XR, others), divalproex sodium (Depakote) and gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise). NSAIDs. Prescription nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs — such as naproxen sodium (Anaprox, Naprelan) — might be helpful, especially if you’re withdrawing from other pain relievers.
What is the new medicine for migraines? The Food and Drug Administration approved the most recent, atogepant (Qulipta), in September 2021. Lasmiditan (Reyvow) is a separate type of treatment that targets the serotonin receptors on brain nerve endings to halt migraine attacks as they occur.
What are the 3 migraine injections?
There are four options currently available for injectable migraine treatment:
- eptinezumab (Vyepti)
- erenumab (Aimovig)
- fremanezumab (Ajovy)
- galcanezumab (Emgality)
What is the best medicine for chronic migraines? – Additional Questions
What do you do when a migraine medication doesn’t work?
If your OTC medicines haven’t worked, your doctor may prescribe stronger medications called triptans, including:
- Almotriptan (Axert)
- Eletriptan (Relpax)
- Frovatriptan (Frova)
- Naratriptan (Amerge)
- Rizatriptan (Maxalt)
- Sumatriptan (Imitrex)
- Zolmitriptan (Zomig)
What is the difference between Nurtec and Qulipta?
Qulipta is taken to prevent migraines and is taken once a day with or without food. Nurtec ODT is taken when you have a migraine (one tablet only over a 24 hour period), with a maximum of 18 tablets over 30 days. To prevent migraines, one tablet of Nurtec ODT is taken every other day.
What is in the migraine cocktail?
The exact medications used in a migraine cocktail can vary, but it typically includes triptans, NSAIDs, and antiemetics. A migraine cocktail is also available in OTC medication. OTC products usually contain aspirin, acetaminophen, and caffeine.
How long does Qulipta take to work?
Qulipta begins working as soon as you take a dose. In studies of the drug, some people reported fewer migraine episodes within 1 week of starting Qulipta. But it can take up to 12 weeks for the drug’s effects to take hold.
What is the quickest way to get rid of a migraine?
Hot packs and heating pads can relax tense muscles. Warm showers or baths may have a similar effect. Drink a caffeinated beverage. In small amounts, caffeine alone can relieve migraine pain in the early stages or enhance the pain-reducing effects of acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) and aspirin.
Why do I wake up with a headache every day?
A number of sleep or health disorders, as well as personal habits, can trigger a headache when you wake up. Sleep apnea, migraine, and lack of sleep are common culprits. However, teeth grinding, alcohol use, and certain medications can also cause you to wake up with a headache.
Can you take traMADol for a migraine?
Conclusions. —Tramadol/APAP reduces the severity of pain, photophobia, and phonophobia associated with migraine headache, but does not reduce migraine-associated nausea. Tramadol/APAP might be an appropriate option for the management of moderate-to-severe migraine headache.
How do you make migraines go away naturally?
18 Remedies to Get Rid of Headaches Naturally
- Drink Water. Inadequate hydration may lead you to develop a headache.
- Take Some Magnesium.
- Limit Alcohol.
- Get Adequate Sleep.
- Avoid Foods High in Histamine.
- Use Essential Oils.
- Try a B-Complex Vitamin.
- Soothe Pain with a Cold Compress.
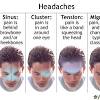
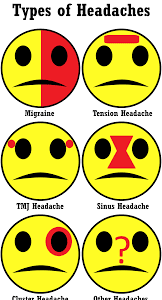
What is the difference between a headache and a migraine?
Headaches cause pain in the head, face, or upper neck, and can vary in frequency and intensity. A migraine is an extremely painful primary headache disorder. Migraines usually produce symptoms that are more intense and debilitating than headaches. Some types of migraines do not cause head pain, however.
What can trigger a migraine headache?
Bright or flashing lights can induce migraines, as can loud sounds. Strong smells — such as perfume, paint thinner, secondhand smoke and others — trigger migraines in some people. Sleep changes. Missing sleep or getting too much sleep can trigger migraines in some people.
What are migraines caused by?
The exact cause of migraines is unknown, but they’re thought to be the result of abnormal brain activity temporarily affecting nerve signals, chemicals and blood vessels in the brain.
What happens in brain during migraine?
One aspect of migraine pain theory explains that migraine pain happens due to waves of activity by groups of excitable brain cells. These trigger chemicals, such as serotonin, to narrow blood vessels. Serotonin is a chemical necessary for communication between nerve cells.
What foods to avoid if you have migraines?
10 Migraine-Triggering Foods
- Excessive coffee.
- Red wine.
- Aged cheeses.
- Chocolate.
- Citrus fruits.
- Aspartame and other artificial sweeteners.
- Yeast.
- Monosodium glutamate (a.k.a. MSG)
Can migraines cause brain damage?
When you look at the population-based evidence, the really good studies, there is no good evidence that those changes in the brain are even lesions, because they don’t cause anything and there is no evidence at all that migraine does excess damage to the brain.
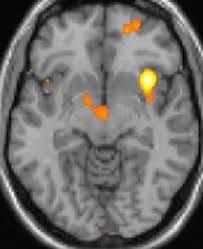
Do migraines show on MRI?
An MRI can’t diagnose migraines, cluster, or tension headaches, but it can help doctors rule out other medical conditions that may cause your symptoms, such as: A brain tumor.
Are migraines a disability?
If you experience chronic migraine that makes it difficult or impossible for you to work you can file a claim for Social Security disability benefits. You will need to provide medical documentation of your illness in order for your claim to be approved.
At what age do migraines stop?
It is rare for Migraine to start later in life, but it does happen. Typically, Migraine becomes less severe and frequent, and may even disappear, by around the age of 50. For some women this is associated with menopause, for others, it may be retirement or reduced stress.