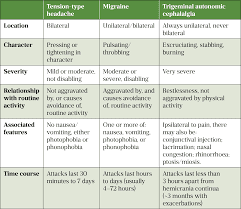
Can postpartum cause migraines? The most common cause of a headache in the postpartum period is an exacerbation of primary headache syndromes, such as migraine, cluster, and tension headaches.
How do you get rid of postpartum migraines? Many new moms worry about medications interfering with breastfeeding, but there are treatments for migraine that won’t appear in breast milk and are safe to take. Several triptans, a migraine-specific medicine, are not contraindicated for breastfeeding, and Tylenol, ibuprofen, and other NSAIDs are safe as well.
Can breastfeeding cause migraines? In the postpartum period, estrogen levels drop dramatically. At the same time, in the early weeks of breastfeeding, oxytocin and prolactin surge. These hormonal fluctuations may lead to headaches. This type of headache is sometimes referred to as a lactation headache.
Is it normal to have headaches everyday postpartum? After the emotional and physical exhaustion of delivering a baby, the last thing you need is a headache. But a headache in the postpartum period is a common complaint. Hormonal changes, dehydration, anesthesia, and sleep irregularity can all contribute to headache after delivery of your precious newborn.
Can postpartum cause migraines? – Additional Questions
How long do postpartum migraines last?
Despite the cause, postpartum headaches should go away within 6 or so weeks of delivering your baby. Most often, postpartum headaches are tension or migraine headaches, which you can treat at home or with the help of your doctor.
When should I worry about postpartum headaches?
Postpartum headaches typically happen right after having a baby, usually within the first six weeks. Sometimes, though, headaches are a sign of something serious. Talk to your doctor immediately if you’re experiencing other symptoms, including: Loss of vision.
Are headaches common while breastfeeding?
They typically begin during the first week after delivery. 1 For the following six weeks, headaches tend to be more painful and last longer than usual. This is likely due to fluctuating hormones after birth. If breastfeeding does help migraines, it’s likely because it helps stabilize estrogen levels.
What is preeclampsia postpartum?
Overview. Postpartum preeclampsia is a rare condition that occurs when you have high blood pressure and excess protein in your urine soon after childbirth. Preeclampsia is a similar condition that develops during pregnancy and typically resolves with the birth of the baby.
How long after delivery can you get preeclampsia?
Most often, symptoms of preeclampsia happen during pregnancy. But some women who develop preeclampsia do so after delivery. This includes some who had normal blood pressure during pregnancy. Postpartum preeclampsia most often happens within a few days after delivery, but it can occur up to 6 weeks later.
Can low iron cause headaches?
A deficiency of iron or vitamins can lead to headaches related to low oxygen levels in the brain. IDA has also been shown to play a role in migraine, especially during menstruation. A rare cause of headaches called CVT is seen in people with conditions that cause their red blood cells to form clots.
What are the 3 stages of iron deficiency symptoms?
This occurs in three stages:
- First stage: Iron stores are depleted.
- Second stage: When iron stores are low, the normal process of making red blood cells is altered.
- Third stage: Iron-deficiency anemia develops because there isn’t enough iron to make hemoglobin for red blood cells.
What does an anemia headache feel like?
The headache connection
If you remember, anemia makes it so your organs don’t get enough blood to function at 100%. When this happens in your brain, the blood vessels in your brain swell and cause the pressure that sets off a headache. This same pressure may also cause lightheadedness or dizziness.
Can low hemoglobin cause migraines?
Conclusion: The present study suggests an association between iron-deficiency anemia, hemoglobin and serum ferritin levels and the incidence of migraine in females.
What does an anemic tongue look like?
Pernicious Anemia Tongue Symptoms
Pernicious anemia causes the tongue’s surface to look smooth and appear red instead of the pinkish color of a normal tongue. The tongue might also appear thick or beefy in texture. Some tongues might even be swollen or seem to have cracks.
What vitamin helps with headaches?
Riboflavin. Better known as vitamin B2, this may make migraines less frequent and less severe for some people. It’s found naturally in foods like: Meat.
Can low vitamin D cause headaches?
To gauge the potential link between vitamin D levels and headaches, researchers divided the population into quartiles by their vitamin D levels and compared the headache risk among the groups. They found that not only were those with the lowest vitamin D levels twice as likely to report chronic headaches.
What deficiencies cause migraines?
Neurologist Dr. Joshua Daniel of Shore Physicians Group said many migraine headache sufferers are found to be deficient in magnesium when they have blood work done.
Can B12 deficiency cause migraines?
According to a 2020 study, headaches were the most common symptom of vitamin B12 deficiency in adolescence. Other research shows that vitamin B12 might help treat chronic migraine. In a 2019 study of 140 people, researchers found that the participants who had migraine also had low blood levels of B12.
How do you feel if your body is low on vitamin D?
Symptoms when vitamin D is low
“Most patients with vitamin D deficiency are asymptomatic, however if you’re exhausted, your bones hurt, you have muscle weakness or mood changes, that’s an indication that something may be abnormal with your body,” says Dr.
What are the 14 signs of vitamin D deficiency?
These include:
- Aching Muscles. Aching muscles can be a sign of vitamin D deficiency because this nutrient is essential for keeping your muscles healthy.
- Painful Bones.
- Fatigue.
- Reduced Endurance.
- Low Moods.
- Problems Sleeping Well.
- Sweaty Head.
- Losing Hair.
How can I check my vitamin D levels at home?
At-home tests typically have you prick and squeeze a finger to collect a smaller blood sample. It’s easier to measure 25-OH D because it lasts longer in the bloodstream, around 14 days. It’s also easier to detect changes in 25-OH D levels associated with vitamin D deficiency.