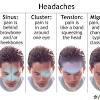
Can a tumor cause ocular migraines? To be diagnosed with an ocular migraine condition, your doctor must rule out any underlying causes for the symptoms you are experiencing such as blood clot, stroke, pituitary tumor, or detached retina. If your retina exam is normal, it is possible that you are experiencing ocular migraines.
Do ocular migraines mean brain tumor? Can a Migraine Cause a Brain Tumor? If you get bad migraines or you have them often, you may worry that if you don’t already have a brain tumor, the migraines might cause one. But research can help put your mind at ease. There is no evidence migraines cause brain tumors.
Can ocular migraines be a symptom of something else? Harsh lighting, long screen time, other visual strain, stress, dehydration, food additives, and other causes all may trigger an ocular migraine, a subtype that focuses in the eye and causes vision changes.
Do brain tumors cause visual auras? Vision changes
Blurry vision, double vision, and loss of vision are all associated with tumors, Schwartz says. You may also see floating spots or shapes—or what’s known as an “aura.”
Can a tumor cause ocular migraines? – Additional Questions
Why am I getting so many ocular migraines?
Common triggers include stress, hormonal changes, bright/flashing lights, drinking alcohol (red wine), changes in the weather, skipping meals/not eating enough, or too much or too little sleep.
What is usually the first symptom of a brain tumor?
Usually, the first sign of a brain tumor is a headache, generally in conjunction with other symptoms.
Can a brain tumor cause kaleidoscope vision?
Brain tumour symptoms can include changes to vision, such as blurred or double vision, abnormal eye movements, restricted field of view and more. It is important to remember that brain tumours are relatively rare, which means it is likely that your symptoms are NOT due to a brain tumour.
Can a brain tumor cause eye flashes?
Another set of symptoms—unexplained speech, vision or hearing problems—can occur when a tumor grows near the areas of the brain that control these functions. A tumor growing near the visual pathways can cause loss of peripheral vision on one side or cause someone to see flashing lights.
What kind of vision problems do brain tumors cause?
If a brain tumor exerts enough pressure on the optic nerve, blindness can occur. For many patients, the loss of vision is gradual, beginning with blurry vision, double vision or an increasing blind spot. As the tumor grows, however, it will compress the optic nerve, resulting in greater vision loss.
What vision problems are associated with brain tumor?
Brain tumors can lead to vision changes such as:
- Blurred or double vision.
- Narrowing of your field of vision.
- Blind spots.
- Difficulty controlling eye movements.
- Unusual eye movements such as flickering of the eyes.
- Increased sensitivity to light.
- Head tilt (caused by trying to see things out of the corner of the eye)
Can an optometrist see a brain tumor?
Eye symptoms of a brain tumour
It is always worth seeing both your GP and an optometrist (optician) to investigate such symptoms. If your doctor suspects the presence of a brain tumour, they will immediately refer you for a scan at a hospital in order to be sure whether or not one is present.
Can an eye doctor tell if you have a brain tumor?
Your eye exam could help to detect if you have a brain tumor. If you have a brain tumor, your eye doctor may notice that you have blurry vision, one eye dilated more than the other or one remains fixed, and they may detect changes to optic nerve color or shape.
Can opticians pick up brain Tumours?
So can an eye doctor detect a brain tumor? An optometrist (also known as an optician) can check for blurred vision and monitor unusual pupil dilation and the colour of the optic nerve. A Visual Fields diagnostic test can assist in the diagnosis. This test is widely available within optometry practices today.
What does a brain tumor headache feel like?
For most individuals, a brain tumor headache is localized to a specific area and is typically worse in the early morning or at night. They can be dull, pressure-like headaches that are made worse by coughing or sneezing. Over time, these headaches stop responding to over-the-counter medication.
How long does it take for symptoms of a brain tumor to show?
The symptoms can develop gradually over some months or even years if the tumour is slow growing. Or quickly over days or weeks if the tumour is fast growing. This video explains the importance of going to your GP if you notice any possible cancer symptoms. It lasts for 42 seconds.
Is neck pain a symptom of brain tumor?
back or neck pain that may extend to the arms or legs, be dull, sharp or burning or be worse at night. weakness. numbness. lack of coordination that is usually on both sides of the body.
Do brain tumors hurt when you press your head?
Brain Cancer Facts
Some brain tumors do not cause headaches at all, since the brain itself isn’t capable of sensing pain. Only when a tumor is large enough to press on nerves or vessels do they cause headache.
How do I know if my headache is a brain tumor?
Symptoms of a brain tumor headache
- headaches that wake you up at night.
- headache pain that changes as you change positions.
- headache pain that doesn’t respond to standard pain relievers such as aspirin, acetaminophen (Tylenol), or ibuprofen (Advil)
- headaches that last for days or weeks at a time.
What is the most common site for head and neck tumors?
The oral cavity was the most frequent anatomical site for the head and neck cancers accounting for 37.3 % of patients (Table 1).
Can brain tumor symptoms come on suddenly?
Signs and symptoms of brain or spinal cord tumors may develop gradually and become worse over time, or they can happen suddenly, such as with a seizure.
What cancers start in the neck?
Types of Head and Neck Cancers Include:
- Oropharyngeal Cancer.
- Hypopharyngeal Cancer.
- Laryngeal Cancer.
- Lip and Oral Cavity Cancer.
- Nasopharyngeal Cancer.
- Paranasai Sinus and Nasal Cavity Cancer.
- Salivary Gland Cancer.
- Squamous Cell Neck Cancer.