Are migraines brain seizures? On the surface, migraines and epileptic seizures look nothing alike. Hyperactivity in brain circuits triggers the characteristic symptoms of seizures, like convulsions and loss of consciousness. A typical migraine, on the other hand, involves a throbbing headache, nausea, and sensitivity to light and sound.
What is Migralepsy? Migralepsy is defined as a seizure triggered by a migraine attack with aura: in particular, the seizure must fulfill the diagnostic criteria for a specific seizure, it has to occur in a patient suffering from migraine with aura (MA), during, or within 1 h of a migraine attack with aura (5).
Can a seizure mimic a migraine? Migraine headaches and seizures share many similar symptoms and often a person with one disorder will experience the other. Seizure auras have many of the same symptoms as migraine auras. Many people who suffer seizures have severe headaches after their seizures because they are misdiagnosed as migraines.
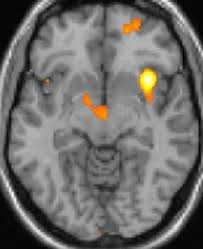
Do migraines show on EEG? In our study, according to headache types, there was a significantly high frequency of EEG abnormalities. Ten (24.4%) patients with migraines with aura had abnormal EEGs, and 12 (11.1%) patients with migraines without aura had abnormal EEGs (Figure 2).
Are migraines brain seizures? – Additional Questions
How long do seizure headaches last?
The pain of a postictal headache is widespread. It can be steady or throbbing and its intensity can range from mild to severe. These headaches usually last between about 6 and 24 hours, or sometimes even longer. They may be quite disabling, causing you to lose additional time out of your normal activities.
What does an occipital seizure look like?
Seizures occurring in the occipital lobe are not common, but they affect your sight. Symptoms might include seeing patterns, flashing lights or colours, or images that appear to repeat before the eyes. There may be other visual effects as well, e.g. partial blindness may occur.
How do you tell if you’ve had a seizure?
What are the symptoms of a seizure?
- Staring.
- Jerking movements of the arms and legs.
- Stiffening of the body.
- Loss of consciousness.
- Breathing problems or stopping breathing.
- Loss of bowel or bladder control.
- Falling suddenly for no apparent reason, especially when associated with loss of consciousness.
How do you tell if it’s a migraine or something more serious?
Signs a Migraine Might Be More Serious
- Intense, continuous nausea and vomiting.
- High fever.
- Stiff neck.
- Head pain that is more severe or different than usual.
- Difficulty speaking.
- Intense confusion.
- Prolonged vision changes.
- Weakness/difficulty moving.
Are migraines similar to epilepsy?
Epilepsy and migraine are both episodic functional disorders in which susceptible brain regions are hyperexcitable and attacks begin with hypersynchronous neuronal firing. In epilepsy, the hypersynchronous activity continues, whereas in migraine with aura (and possibly also in migraine without aura) there is CSD.
What drug treats epilepsy and migraines?
Topiramate: a medicine to treat epilepsy and migraine – NHS.
Are migraines like small strokes?
Migraine can sometimes be mistaken for a stroke caused by bleeding on the brain, called a subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH), which is often characterised by a sudden, very severe headache. Unlike SAH, migraine headache is usually one-sided and throbbing, slow to come on and lasts for a shorter period of time.
What are non epileptic seizures?
PNES are attacks that may look like epileptic seizures but are not epileptic and instead are cause by psychological factors. Sometimes a specific traumatic event can be identified. PNES are sometimes referred to as psychogenic events, psychological events, or nonepileptic seizures (NES).
Does an EEG show past seizures?
The EEG generally records brain waves between seizures, called interictal brain waves. These waves may or may not show evidence of seizure activity.
What can be mistaken for a seizure?
Movement disorders — Tics, tremors, and other involuntary movements can look like a myoclonic seizure or focal seizure, but they may be caused by things like Tourette’s syndrome, Parkinson’s disorder, Huntington’s disease, and other disorders that affect the brain.
Does epilepsy show up on MRI?
Uses of MRI
Structural imaging is used to look for a potential structural cause of someone’s epilepsy, such as a scar on the brain. However, for many people with epilepsy, no structural cause for their epilepsy can be found, and so their MRI results are said to be ‘normal’.
Do blood tests show epilepsy?
Epilepsy is diagnosed by a neurologist. To start, they’ll perform a neurological exam to assess how well your nervous system is working. This includes questions about your symptoms, as well as your medical history. A neurologist will also use blood tests, imaging scans, and EEGs to determine if you have epilepsy.
Can a doctor tell if you’ve had a seizure?
Electroencephalogram (EEG) – Using electrodes attached to your head, your doctors can measure the electrical activity in your brain. This helps to look for patterns to determine if and when another seizure might occur, and it can also help them rule out other possibilities.
Can a blood test tell if you had a seizure?
The blood test, which must be used within 10 to 20 minutes after a seizure, can identify the types of seizures called generalized tonic-clonic seizures and complex partial seizures in both adults and older children.
How do neurologists test for seizures?
An electroencephalogram (EEG).
In this test, doctors attach electrodes to your scalp with a paste-like substance. The electrodes record the electrical activity of your brain, which shows up as wavy lines on an EEG recording. The EEG may reveal a pattern that tells doctors whether a seizure is likely to occur again.
Can you drive if you have seizures?
Every state regulates driver’s license eligibility of persons with certain medical conditions. The most common requirement for people with epilepsy is that they be seizure free for a specific period of time and submit a physician’s evaluation of their ability to drive safely.
Do seizures show up on CT scans?
A CT scan is a type of X-ray that creates detailed images of tissue and internal organs. CT scans can help doctors identify any brain abnormalities that might be causing seizures, such as scar tissue, tumors, or malformed blood vessels. They can also identify any spinal fluid circulation problems.