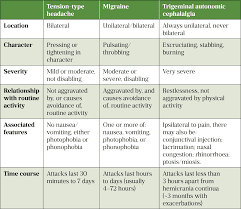
Why do I get migraines and neck pain? An important brain area in migraine is the trigeminocervical complex, a hub for pain nerves of the face and upper neck. Researchers think that this entire complex is activated during a migraine, which would explain why the pain extends into the neck for some patients.
Is migraine related to neck pain? Recent research found that neck pain is usually a symptom of migraine and not a cause. Migraine typically originates in the brain. Cervicogenic headaches may also induce neck pain, but are rooted in the cervical spine or base of the skull.
How do you stop a migraine and neck pain?
Several conditions can cause neck pain and headache to occur together.
Just remember to stop a treatment if it makes your pain worse.
- Apply firm pressure.
- Try heat therapy.
- Use an ice pack.
- Maintain good posture.
- Sleep, but don’t oversleep.
- Find the right pillow.
- Keep a daily journal.
- Visit a physical therapist.
What kind of migraine starts in the neck? A cervicogenic headache starts in the cervical spine—your neck. Sometimes these headaches mimic migraine headache symptoms. Initially, pain may begin intermittently, spread to one side (unilateral) of the patient’s head, and become almost continuous.
Why do I get migraines and neck pain? – Additional Questions
When should I worry about headaches and neck pain?
Your headache pain may be serious if you have: sudden, very intense headache pain (thunderclap headache) severe or sharp headache pain for the first time. a stiff neck and fever.
What does a brain Tumour headache feel like?
Every patient’s pain experience is unique, but headaches associated with brain tumors tend to be constant and are worse at night or in the early morning. They are often described as dull, “pressure-type” headaches, though some patients also experience sharp or “stabbing” pain.
Can migraines start in the back of your neck?
In most cases, cervicogenic headaches develop on one side of the head, starting from the back of the head and neck and radiating toward the front. Some other symptoms of a cervicogenic headache include: pain around the eyes.
Is cervicogenic headache serious?
Although rare, it can be a sign of a tear in one of the neck arteries. This is a common cause of stroke, especially in people under age 45. If you notice any of these signs with a headache, seek emergency care right away: Sudden, severe neck pain.
How long do cervicogenic headaches last?
A “cervicogenic episode” can last one hour to one week. Pain typically is on one side of the head, often correlating with the side of the neck where there is increased tightness. Almost certainly, range of motion will be compromised. Common causes of CGH can be chronic: poor posture, as noted above, or arthritis.
Can a pinched nerve in the neck cause migraines?
Does a Pinched Nerve in the Neck Cause Headaches? One of the more common medical causes of headaches are pinched nerves in the neck. Pinched nerves in the neck cause headaches by compressing the nerve which generates a feeling of pain along the nerve’s pathway.
What does severe neck pain indicate?
Neck pain can last from days to years, depending on the cause. Common causes include osteoarthritis, spinal stenosis, herniated disc, pinched nerve, mental and physical stress and strain, poor posture, tumors and other health conditions.
What type of doctor should I see for cervicogenic headache?
Physical therapy and an ongoing exercise regimen often produce the best outcomes. Other providers that may need to be involved in management of cervicogenic headache include physical therapists, pain specialists (who can do the injections/blocks), and sometimes neurosurgeons or orthopedic surgeons.
Can arthritis in your neck cause migraines?
The answer is yes. Certain types of arthritis, including arthritis of the spine, can trigger a migraine for some people. Arthritis causes inflammation of the joints, which can lead to pain and joint disease. Other symptoms include swelling, stiffness, and decreased range of motion.
What are the symptoms of osteoarthritis in the neck?
Neck Osteoarthritis Symptoms
- Neck pain that worsens with activity performed when a person is upright.
- Neck pain that radiates to the arm or shoulder.
- Numbness, tingling, and weakness in the arms, hands, fingers, legs, or feet.
- Weakness in the legs, trouble walking, loss of balance.
- Loss of bladder or bowel control.
Does MRI show arthritis in neck?
MRI and other advances in medical imaging have made it increasingly possible to detect arthritis in its early stages and assess its severity. MRI scans are a powerful tool for diagnosing arthritis, as they are more sensitive than traditional X-rays and ultrasound imaging.
What does an arthritis headache feel like?
Arthritis Headaches Symptoms
Unlike a normal headache, a neck arthritis headache typically begins with pain in your neck. From there, the pain will move up the back of your head until it reaches the top. In addition, the pain will usually be worse on one side of your head, and you won’t have pain in your temple region.
What autoimmune disease causes headaches?
Among secondary forms, headache has been suggested to be a neurological manifestation of many immunological/autoimmune disorders, both those primarily involving the central nervous system (CNS), such as multiple sclerosis, and those systemic, such as systemic lupus erythematosus.
Can an xray show arthritis in the neck?
X-rays of the spine, neck, or back may be performed to diagnose the cause of back or neck pain, fractures or broken bones, arthritis, spondylolisthesis (the dislocation or slipping of 1 vertebrae over the 1 below it), degeneration of the disks, tumors, abnormalities in the curvature of the spine like kyphosis or
Are migraines a symptom of rheumatoid arthritis?
Migraine is highly frequent in rheumatoid arthritis patients, especially migraine with aura. The presence of rheumatoid activity, fibromyalgia and secondary Sjogren’s syndrome, elevated ESR and CRP are associated with functional losses in rheumatoid arthritis patients with migraine, especially migraine with aura.
Are migraines linked to autoimmune?
Recent studies have suggested that immunological dysfunction or autoimmunity could play an integral role in the pathophysiology of migraine. Our recent experiments showed decreased CD4+CD25+ cell population in peripheral blood of migraineurs compared to the healthy volunteers.
What is rheumatic headache?
Abstract. Headaches are a common, but under-recognized and understudied symptom in the context of the rheumatic diseases. They can result from intracranial pathology, such as parenchymal and meningeal inflammation, thrombosis, space-occupying lesions, and more.