Can a neurologist help with migraines? How can a neurologist help with migraine? Neurologists specialize in disorders of the nervous system, including the brain. Migraine is a neurological disorder. A neurologist can help make an accurate diagnosis of migraine, as well as rule out any other potential neurological condition that may cause similar symptoms.
What do I tell my neurologist about migraines? Explain your pain.
Be prepared to tell them what your headache feels like, where the pain is on your head, how long it lasts, when the issues happen, and if you know any possible triggers. You may want to keep a headache diary so that you can track these things. Bring it to your appointment for reference.
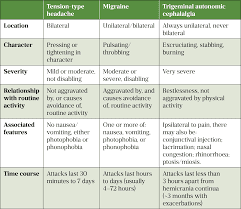
Do neurologists handle headaches? “Patients should see a neurologist for any headache that is disabling,” McLauchlin said. “This applies to you if you have to stop what you are doing and lie down during a headache.” If your headaches cause pain in other areas or if the pain is on only one side of the head, you may need to see a neurologist.
What should I ask my neurologist for migraines?
Questions to Ask Your Doctor About Migraines
- How can I pinpoint what triggers my headache?
- What should I keep track of in a headache diary?
- Could any of my medicines (such as birth control pills) be making my migraine headaches worse?
- Is there a chance my migraine symptoms might go away in a few years?
Can a neurologist help with migraines? – Additional Questions
Can an MRI detect migraines?
An MRI can’t diagnose migraines, cluster, or tension headaches, but it can help doctors rule out other medical conditions that may cause your symptoms, such as: A brain tumor. An infection in your brain, called an abscess. The buildup of fluid in the brain, called hydrocephalus.
What does a neurologist do on your first visit?
During your first appointment, a Neurologist will likely ask you to participate in a physical exam and neurological exam. Neurological exams are tests that measure muscle strength, sensation, reflexes, and coordination. Because of the complexity of the nervous system, you may be asked to undergo further testing.
Is there a test for migraines?
There’s no specific test to diagnose migraines. For an accurate diagnosis to be made, a GP must identify a pattern of recurring headaches along with the associated symptoms. Migraines can be unpredictable, sometimes occurring without the other symptoms. Obtaining an accurate diagnosis can sometimes take time.
What questions should I ask my headache doctor?
Headache – what to ask your doctor
- Are there foods that I should stay away from that may make my headaches worse?
- Are there medicines or conditions in my home or work that may be causing my headaches?
- Will alcohol or smoking make my headaches worse?
- Will exercise help my headaches?
Do migraines show up on CT scan?
Medical professionals will not use a CT scan to diagnose migraine headaches. If a person is experiencing migraine, a CT scan will rarely show the cause of the pain. However, a doctor may order a CT scan or similar imaging test to rule out other causes of a person’s headaches.
How many migraines a month is normal?
Most people experience migraine episodes 2-4 times a month while others may only have 1-2 episodes a year. Migraines can be classified into distinct categories based on the number of episodes: Acute or episodic migraine: 1-14 of fewer migraine headaches a month.
Can you get on disability for migraines?
The bottom line. If you’re unable to work due to chronic migraine, you can apply for disability benefits. You need to have enough work credits and evidence that you can’t work anymore due to your migraine symptoms. Migraine disability may be difficult to prove, but it can be done.
Are migraines considered a disability?
Does that mean migraine headaches qualify you for disability benefits? Possibly. The Social Security Administration (SSA) oversees disability benefits. They don’t list migraine as a condition that qualifies for disability.
Why do I keep getting migraines everyday?
Every person who has migraines has different triggers, but common ones include a lack of sleep, caffeine, and being under stress. Most people who get chronic migraines are women. This may be because hormone changes are another well-known cause.
How many is too many migraines?
Migraine is considered chronic when people have 15 or more headache days per month, with at least 8 of those days meeting criteria for migraine. Chronic migraine can be a very disabling condition. Development of chronic migraine has been associated with a number of potentially treatable risk factors.
How do you permanently cure a migraine?
Consider the basics:
- Be consistent. Eat at about the same time every day.
- Don’t skip meals. Fasting increases the risk of migraines.
- Keep a food journal. Keeping track of the foods you eat and when you experience migraines can help identify potential food triggers.
- Avoid foods that trigger migraines.
Do migraines get worse with age?
Migraines can begin at any age, though the first often occurs during adolescence. Migraines tend to peak during your 30s, and gradually become less severe and less frequent in the following decades.
Do migraines lead to Alzheimer’s?
Researchers have found a strong association between experiencing migraine attacks and increased risk of developing dementia, particularly Alzheimer’s disease.
What can trigger a migraine headache?
What triggers a migraine?
- Emotional stress. Emotional stress is one of the most common triggers of migraine headaches.
- Missing a meal.
- Sensitivity to specific chemicals and preservatives in foods.
- Caffeine.
- Daily use of pain-relieving medications.
- Hormonal changes in women.
- Light.
Will I have migraines for the rest of my life?
Migraines often run in families, and can start as early as elementary school but most often in early adulthood. They often fade away later in life, but can strike at any time.
How long is too long for a migraine?
How long is too long? If a migraine headache lasts longer than 72 hours without responding to regular migraine medication, the person may need additional treatment. Anyone who has experienced this pain for longer than 3 days should speak with a doctor as soon as they can.
When is a migraine serious?
You should call 999 for an ambulance immediately if you or someone you’re with experiences: paralysis or weakness in 1 or both arms or 1 side of the face. slurred or garbled speech. a sudden agonising headache resulting in a severe pain unlike anything experienced before.