What is the success rate of Botox for migraines? Approximately 65% of people see improvement in their migraine symptoms following Botox headache treatment. In fact our patients have had such success with Botox treatment that the percentage realistically is closer to 95%!
Does Botox actually help migraines? Botulinum toxin treatments have been proved effective in clinical trials, and are one way to treat chronic migraines. Other medications, and lifestyle changes, might be recommended. If your doctor determines that you have chronic migraines, you might be a candidate for this treatment.
Can Botox for migraines make them worse? For some people, botulinum toxin injections (Botox®) will help relieve a good portion of their headache symptoms, headache severity, and headache frequency. For some people, botulinum toxin injections will make their headache symptoms, headache severity, and headache frequency worse.
How long does it take for Botox to take effect for migraines? Botox Treatment
You could see results 2 to 3 weeks after your first treatment. You should only get this type of Botox treatment from a doctor who’s trained to give these shots for chronic migraine headaches rather than for wrinkles or other cosmetic uses.
What is the success rate of Botox for migraines? – Additional Questions
What should you not do after Botox for migraines?
To avoid infection and allow the complete absorption of the drug into the areas injected, it is best to avoid the following during the first 24 hours: Vigorous exercise (e.g. gym, jogging) Hair washing – you may want to wash your hair the day before the appointment. Skin cleansing in areas injected.
What should you not do before Botox for migraines?
You don’t need to do anything to prepare, but your doctor may ask you to stop taking certain medications a few days prior to the injection. You should also inform your doctor if you’ve had a Botox injection in the past four months, even if it wasn’t an injection for migraines.
How long does migraine Botox last?
After several months, the nerves sprout new pain fibers, and the headaches tend to return. The Botox effect usually lasts about two-and-a-half months. Because injections are repeated no sooner than every three months, some people need other headache treatment for the last two weeks of a Botox cycle.
How many units of Botox is used for migraines?
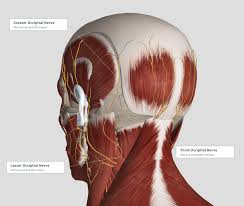
The recommended total dose of Botox (onabotulinumtoxinA) for chronic migraine prevention is 155 Units administered intramuscularly (into the muscle). This is given as 0.1 mL (5 Units) injections divided across 7 specific head and neck muscle areas, for a total of 31 individual injections per session.
How often can you get Botox for migraines?
The person doing your treatment will have been trained to provide Botox for chronic migraine. Injections are given every 12 weeks.
Which treatment is best for migraine?
Triptans. Prescription drugs such as sumatriptan (Imitrex, Tosymra) and rizatriptan (Maxalt, Maxalt-MLT) are used to treat migraine because they block pain pathways in the brain. Taken as pills, shots or nasal sprays, they can relieve many symptoms of migraine.
Can Botox cause neurological problems?
FDA has reported adverse events after BoNT injection affecting nervous system far from initial site of injection such as speech disorder, nystagmus, restless leg syndrome, and even coma. Central nervous system involvement included 23.5% of serious and 24.9% of non-serious events (1).
Who shouldn’t Botox?
If you are in poor general health, your skin is very thick or you have existing muscle weakness in the proposed injection site, you may not be a good candidate for Botox. Patients with sensitive skin may experience an allergic reaction at the injection site.
Can Botox seep into the brain?
It is one of UK’s most popular cosmetic treatments: the “no-scalpel facial”, smoothing out the foreheads of everyone from yummy mummies to stressed-out politicians. But new research suggests that the deadly poison in Botox jabs may actually be able to spread from the face to the brain.
What happens if Botox hits a nerve?
The botulinum toxins cancel nerve signals to the muscles, creating paralysis that can last for months. Given its extraordinary toxicity, doses are typically measured in trillionths of a gram, and targets are carefully chosen to silence only the desired motor nerves.
What are the 3 common side effects of Botox?
Possible side effects and complications include:
- Pain, swelling or bruising at the injection site.
- Headache or flu-like symptoms.
- Droopy eyelid or cockeyed eyebrows.
- Crooked smile or drooling.
- Eye dryness or excessive tearing.
Are there any long term side effects of Botox?
There are no long-term or life-threatening adverse effects related to botulinum toxin treatment for any cosmetic indications. Moreover, the risk of possible complications can be reduced by means of a thorough analysis of the patient’s medical history and the use of the appropriate dose and technique for the injection.
What are the long term side effects of Botox?
The longest follow-up study of 45 patients continuously treated with botulinum toxin for 12 years identified 20 adverse events in 16 patients including dysphagia, ptosis, neck weakness, nausea/vomiting, blurred vision, marked weakness, chewing difficulties, hoarseness, edema, dysarthria, palpitations, and general
Can you stop Botox once you start?
If you stop BOTOX treatments after many years of regular injections, the only effect will be that your wrinkles will return, albeit a bit more slowly than if you had not been using BOTOX. It’s true: Even after you stop, you will still look younger than you would have if you had never been injected.
Does Botox harm the liver?
Answer: Botox not harmful to liver or kidneys
It is designed not to travel systemically. The quantity of Botox even if it does get into the blood stream is very small. As of this writing, the drug has been used millions of times without reports of kidney or liver damage.
Can Botox affect your heart?
The research shows that having facial Botox injections for cosmetic reasons can also produce side-effects including muscle stiffness, pain, dizziness and even a heart attack.
Can Botox cause blood clots?
Botox is a neurotoxic protein and acts by paralysing the muscles around where it is injected. It is therefore unlikely to be the cause of blood clots.