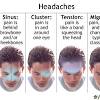
Is taking magnesium good for migraines? Research on magnesium has found it to be a potentially well-tolerated, safe and inexpensive option for migraine prevention, while it may also be effective as an acute treatment option for headaches including migraines, tension- type headaches and cluster headaches, particularly in certain patient subsets.
How much magnesium should I take for migraines? What form of magnesium is best for migraine? Magnesium oxide is frequently used in pill form to prevent migraine, usually at a dose of 400-600 mg per day. Acutely, it can be dosed in pill form at the same dosage or given intravenously as magnesium sulfate at 1-2 gm.
What type of magnesium is good for migraines? Other studies have also suggested that the magnesium levels in a person’s brain may be low during a migraine. The American Migraine Foundation suggest taking a 400–500 milligram (mg) supplement of magnesium oxide daily to prevent migraines.
What is the fastest way to cure a migraine?
In this Article
- Try a Cold Pack.
- Use a Heating Pad or Hot Compress.
- Ease Pressure on Your Scalp or Head.
- Dim the Lights.
- Try Not to Chew.
- Hydrate.
- Get Some Caffeine.
- Practice Relaxation.
Is taking magnesium good for migraines? – Additional Questions
What deficiencies cause migraines?
People need vitamin D to absorb magnesium, and because magnesium deficiency may also contribute to migraine headaches, a lack of vitamin D could further increase the likelihood of migraine episodes.
Does magnesium glycinate help with migraines?
How can it help? Experts think magnesium may help prevent the wave of brain signaling, called a cortical spreading depression, that is thought to cause migraine. It can also reduce pain during an attack by blocking pain-transmitting chemicals in the brain.
Which is better magnesium citrate or magnesium oxide?
Orally, magnesium citrate is the best absorbed form (but it’s bonded to a big molecule so there is a smaller amount of magnesium by weight). Mg oxide is the most poorly absorbed form but has the highest Mg per weight, so actually you may get more elemental magnesium out of the same dose of Mg oxide vs.
What is the difference between magnesium citrate and magnesium glycinate?
Magnesium citrate is a more common choice if you want to maintain magnesium levels for general whole-body health. On the other hand, magnesium glycinate has less bioavailability but can have a calming effect.
Why is B2 good for migraines?
In the body, vitamin B2 (riboflavin) participates in many metabolic processes. Specifically, this water-soluble vitamin may play a role in pathways involved in the development of migraine ( 5 ). For example, migraine episodes are thought to be associated with oxidative stress and brain inflammation.
How much magnesium and b2 should I take for migraines?
Based on the clinical evidence to date, physicians can safely recommend 400 mg/d of riboflavin and 200-400 mg/d of elemental magnesium to patients who suffer migraines often enough to make daily prophylaxis a reasonable choice. Dr.
How much B12 should I take to prevent migraines?
The beneficial effects in reducing migraine frequency appeared after a month of daily doses of 400 mg, and increased over the next two months, researchers said. The 400 mg daily dose is 200 times the recommended daily allowance of this vitamin.
Does B12 help with migraines?
According to a 2020 study, headaches were the most common symptom of vitamin B12 deficiency in adolescence. Other research shows that vitamin B12 might help treat chronic migraine. In a 2019 study of 140 people, researchers found that the participants who had migraine also had low blood levels of B12.
What can I take daily to prevent migraines?
Propranolol. Propranolol is a medicine traditionally used to treat angina and high blood pressure, but it’s also been shown to effectively prevent migraines. It’s usually taken every day in tablet form.
How much vitamin D should I take for migraines?
In a number of studies, vitamin D level was negatively correlated with frequency of headaches. The present findings show that supplementation with this vitamin in a dose of 1000-4000 IU/d could reduce the frequency of attacks in migraineurs.
Can low iron cause migraines?
A deficiency of iron or vitamins can lead to headaches related to low oxygen levels in the brain. IDA has also been shown to play a role in migraine, especially during menstruation.
What does iron deficiency headache feel like?
The headache connection
If you remember, anemia makes it so your organs don’t get enough blood to function at 100%. When this happens in your brain, the blood vessels in your brain swell and cause the pressure that sets off a headache. This same pressure may also cause lightheadedness or dizziness.
What vitamin helps with headaches?
Riboflavin. Better known as vitamin B2, this may make migraines less frequent and less severe for some people. It’s found naturally in foods like: Meat.
What does an anemic tongue look like?
Pernicious Anemia Tongue Symptoms
Pernicious anemia causes the tongue’s surface to look smooth and appear red instead of the pinkish color of a normal tongue. The tongue might also appear thick or beefy in texture. Some tongues might even be swollen or seem to have cracks.
What do nails look like with anemia?
Spoon nails (koilonychia) are soft nails that look scooped out. The depression usually is large enough to hold a drop of liquid. Often, spoon nails are a sign of iron deficiency anemia or a liver condition known as hemochromatosis, in which your body absorbs too much iron from the food you eat.
What are the 3 stages of iron deficiency symptoms?
This occurs in three stages:
- First stage: Iron stores are depleted.
- Second stage: When iron stores are low, the normal process of making red blood cells is altered.
- Third stage: Iron-deficiency anemia develops because there isn’t enough iron to make hemoglobin for red blood cells.
What does anemia fatigue feel like?
Anemia is a condition in which you lack enough healthy red blood cells to carry adequate oxygen to your body’s tissues. Having anemia, also referred to as low hemoglobin, can make you feel tired and weak. There are many forms of anemia, each with its own cause.