Does nexplanon cause migraine? Nexplanon and Headaches
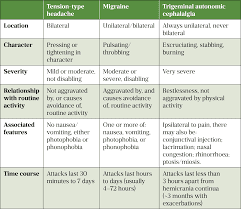
Headaches are the most common side effect of Nexplanon, reported in 25% of women in clinical trials. Side effects also include migraine headaches, which cause symptoms like nausea, vomiting, light-sensitivity, throbbing pain, and visual disturbances.
Can the implant cause migraines? Dental implants are made of titanium and can cause symptoms – including migraines – in people with metal allergies. That means the cause of the migraine isn’t the dental implant itself, but rather, the allergic reaction to it.
Which birth control is least likely to cause migraines? There is general consensus that progesterone-only contraceptives are safe for use in women who have migraine with aura, even in the presence of other risk factors for stroke (Table 2).
Can arm implant cause headaches? But most people on the implant get lighter periods, or their periods stop altogether while they have the implant. Other possible side effects that aren’t as common include headaches, breast pain, and nausea. There may also be temporary pain, bruising, or an infection on your arm where you got the implant.
Does nexplanon cause migraine? – Additional Questions
Do Nexplanon headaches go away?
Changes to your periods is one of the most common side effects of Nexplanon. It’s also the top reason people might have their Nexplanon implant removed. You might also experience headache, weight gain, or acne. Most of the common side effects improve within a few months.
Can the implant cause severe headaches?
Surgical complications: A dental implant is a surgical procedure, and that can come with some side effects, including headaches. Any damage to the sinus cavity or the surrounding nerves could result in facial or head pain. In very rare cases there may be some nerve damage.
Is a headache normal after implant?
If the patient has undergone an implant and has a bad bite or jaw misalignment, migraines or tension headaches are common. Dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint in the jaw may lead to a headache. A mild headache occurs mainly on the side of the temples or head. Moreover, teeth grinding also causes TMJ.
Why do implants cause headaches?
Dental implants are a great solution for replacing missing teeth, but they can cause headaches too. This is because they are placed into the jawbone and the surrounding nerves. Dental implant surgeries are a great solution for replacing missing teeth, but they can cause frequent headaches too.
What are the side effects of titanium implants?
One of the causes of implant failure can be attributed to allergic reactions to titanium. There have been reports of hypersensitive reactions such as erythema, urticaria, eczema, swelling, pain, necrosis, and bone loss due to titanium dental implants [15, 67, 68].
How do you know if you’re allergic to titanium?
It’s possible to detect a titanium allergy ahead of time with a MELISA test. This type of blood test isolates your white blood cells, exposes them to titanium and measures the immune response to titanium.
How do you know if your body is rejecting titanium?
Seminal studies cited by the International Journal of Implant Dentistry report that titanium allergy symptoms include: Erythema (skin redness, in this case, in the tissues around the implant) Urticaria (hives that may be seen on the skin or gum surface) Eczema (itchy inflammation of the skin or gum tissue)
What happens when your body rejects an implant?
Redness, swelling, inflammation, and bleeding around the implantation site is a bad sign after the initial few days. Infections can and do occur—especially in smokers, people with an autoimmune disease or diabetes, and those with poor oral hygiene.
What happens when your body rejects a metal implant?
The clinical presentation of patients with metal implant reactions is often nonspecific. Patients can present with localized dermatitis or rashes but also with systemic eczematous dermatitis. Swelling, pain, draining sinuses, and inflammation at the implant site may mimic infection.
How do you know if your body is rejecting an implant?
Some signs of allergic reactions include loss of taste, swelling around the gums, and a tingling sensation. Sudden allergic reactions are a sign of dental implant failure because they indicate that your body is rejecting the implant.
Why does metal in your body hurt when it rains?
Our body is 60% water and water is hard to heat. Metal is dense and can hold heat. If metal in the body is covered by skin, like a plate in the ankle, thin skin is against thick metal competing for the heat.
How do you know if your body is rejecting metal?
Your body treats the offending substance like a foreign invader and quickly mounts an immune response. The result: redness, itching, swelling or a rash, with skin blistering or scaling at the site. The symptoms of a metal allergy range from mild to severe.
Can you be allergic to the contraceptive implant?
Some pain, bruising, and swelling at the site are common side effects of the birth control implant. But an allergic reaction to the implant is rare, with only three cases reported. There’s a higher chance of being allergic to the anesthesia used to numb the area than to the implant itself.
Can your body reject metal years later?
‘Over time their body becomes sensitised to react to it and so when it comes to later in life and needing an implant — many of which contain nickel or metals that the body’s immune system “sees” as nickel — they reject the implant.
What is a Melisa test?
MELISA is an optimised, clinically validated blood test which measures hypersensitivity to multiple metals from a single sample. MELISA can also to help in the diagnosis of active Lyme disease.
What is LTT blood test?
The lymphocyte transformation test (LTT) measures the proliferation of T cells to a drug in vitro–from which one concludes to a previous in vivo reaction due to a sensitization.
Can you be allergic to titanium implant?
Clinical Characteristics of Hypersensitivity to Titanium. Researchers have described various clinical manifestations in patients with allergies to titanium including episodes of hives, eczema, edema, reddening, and itching of the skin or mucosa, which may be localized, or generalized.