Does exercise help migraines go away? There’s evidence to suggest regular exercise can help reduce the frequency of headache attacks. Not only does exercise reduce stress, a common migraine trigger, but it also helps with sleep and improves your mood.
What is the fastest way to resolve a migraine? Hot packs and heating pads can relax tense muscles. Warm showers or baths may have a similar effect. Drink a caffeinated beverage. In small amounts, caffeine alone can relieve migraine pain in the early stages or enhance the pain-reducing effects of acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) and aspirin.
Which exercise is best for headache? Gently pull the head to the right, and you should feel a pull along the left shoulder and neck. Hold this position for 30 seconds and then return to mid-line. Repeat this exercise on the other side. Repeat 2-3 times on each side.
Is walking good for a migraine? Which types of exercises are beneficial for migraine? Studies have found that regular practice of mild to moderate aerobic exercises, such as brisk walking, jogging, swimming, cycling, dancing, jumping rope, etc., are effective in reducing migraine symptoms.
Does exercise help migraines go away? – Additional Questions
What food gets rid of migraines?
Discover 11 foods that can help migraines go away
- Spinach could help migraines go away. This dark leafy green vegetable is particularly rich in magnesium.
- Kale might help migraineurs.
- Collard, mustard, and turnip greens.
- Almonds.
- Avocados.
- Dark Chocolate.
- Fatty fish.
- Flax seeds.
What causes migraines to start?
Stress at work or home can cause migraines. Sensory stimuli. Bright or flashing lights can induce migraines, as can loud sounds. Strong smells — such as perfume, paint thinner, secondhand smoke and others — trigger migraines in some people.
Can lack of exercise cause migraines?
Associations between physical exercise and migraine—epidemiological evidence. Various large population-based studies have concluded that low physical activity levels are associated with higher prevalence and frequency of migraine and other headaches [13,14,15].
Should I exercise if I have a headache?
You Have a Headache
Exercise reduces stress and improves cardiovascular fitness, so it may soothe the pain right out of your head.
Will exercise make a migraine worse?
Regular exercise is associated with a reduction in the frequency and intensity of migraines, says Jennifer Kriegler, MD, a neurologist at the Cleveland Clinic in Ohio. A good rule of thumb: Don’t exercise if you’re in the middle of a migraine attack, as it can make the pain worse, Dr. Kriegler says.
Does deep breathing help migraines?
Out of these four methods, slow deep breathing is the most successful in reducing stress and has the best outcomes for helping with migraines and headaches. The technique most recommended to follow is very simple: 4 seconds of inhalation, followed by 4 seconds of exhalation, repeated for a minimum of 1 minute.
How long can a migraine last?
A migraine can last anywhere from 4 to 72 hours. It can be difficult to predict how long an individual migraine will last, but charting its progress may help. Migraines can usually be divided into four or five distinct stages.
Is it good to sleep when you have a migraine?
Sleep in migraine
Excessive sleepiness may be part of the premonitory phase before a migraine attack, or a symptom following the attack. Sleep can also be very helpful during a migraine attack, and may often help stop the attack, particularly in children.
What are the 3 types of migraines?
The most common are migraine with aura (also known as a classic migraine) and migraine without aura (or common migraine). Other types include: Menstrual migraine.
What are the four stages of a migraine?
Migraines, which often begin in childhood, adolescence or early adulthood, can progress through four stages: prodrome, aura, attack and post-drome. Not everyone who has migraines goes through all stages.
What happens in brain during a migraine?
One aspect of migraine pain theory explains that migraine pain happens due to waves of activity by groups of excitable brain cells. These trigger chemicals, such as serotonin, to narrow blood vessels. Serotonin is a chemical necessary for communication between nerve cells.
Why do I get so tired before a migraine?
Migraine symptoms may start one to two days before the headache itself. This is referred to as the “prodrome” stage. During this stage, many people also experience fatigue, depression, and low energy. When the headache hits, it’s referred to as the “attack” phase.
What’s the difference between a headache and a migraine?
Headaches cause pain in the head, face, or upper neck, and can vary in frequency and intensity. A migraine is an extremely painful primary headache disorder. Migraines usually produce symptoms that are more intense and debilitating than headaches. Some types of migraines do not cause head pain, however.
What part of your head hurts when you have a migraine?
A migraine is usually an intense pounding headache that can last for hours or even days. The pounding or pulsing pain usually begins in the forehead, the side of the head, or around the eyes. The headache gradually gets worse.
What do you say when you call in sick with a migraine?
What to say – long version: “I’m sorry I can’t make it into work today. I’ve got a severe migraine attack, a condition my neurologist has diagnosed. I can’t predict how long it will last, but as soon as I feel better, I will begin to make up my work.
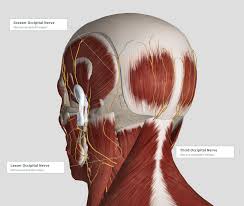
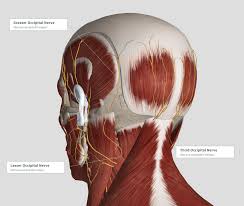
Where are stress migraines located?
Where do they hurt? It can hurt all over your head, but you’ll most likely feel a band of pain around your forehead or the back of your head or around your neck. The headache does not get worse with activity. Your jaw, shoulders, neck, and head may also be tender.
How do you get rid of a migraine that won’t go away?
placing a warm or cool pack on the affected area to help relieve pressure and lessen muscle tension. taking over-the-counter pain medications, such as aspirin, acetaminophen, or ibuprofen. taking triptans, a prescription medication that aims to treat migraines. resting in a cool, dark, quiet room.