Do psychedelic mushrooms help with migraines? Psilocybin may increase nitric oxide levels, triggering headaches in some individuals. But in people with migraine, psilocybin may help. In a recent study, researchers found that a single dose of psilocybin could reduce migraine frequency by 50% for at least 2 weeks.
What mushrooms are good for migraines? Reishi is a traditional medicine for treating migraines in East and Central Asia.
Can psychedelics cure migraine? Primarily, psilocybin, lysergic acid diethylamide, and related psychedelic tryptamines were reportedly effective for both prophylactic and acute treatment of cluster headache and migraines.
How do you deal with chronic migraines?
Here are some further coping tips I have for people who suffer from chronic migraine.
- Get aerobic exercise.
- Try relaxation exercise.
- Stick to a regular sleep schedule.
- Take magnesium supplements.
- Avoid food triggers.
- Avoid caffeine.
- Consider supplements.
- Consider preventive treatments.
Do psychedelic mushrooms help with migraines? – Additional Questions
What is the fastest way to cure a migraine?
In this Article
- Try a Cold Pack.
- Use a Heating Pad or Hot Compress.
- Ease Pressure on Your Scalp or Head.
- Dim the Lights.
- Try Not to Chew.
- Hydrate.
- Get Some Caffeine.
- Practice Relaxation.
How do people live with daily migraines?
Life with an Invisible Illness: What I’ve Learned from Living
- Approach things positively. It’s understandable to feel angry, defeated, or lost.
- Listen to your body.
- Don’t blame yourself.
- Educate those around you.
- Learn to let people go.
- Celebrate your progress.
- Don’t be afraid to ask for help.
- Believe in yourself.
Can chronic migraine be cured?
Migraine is a treatable disease. Treatment cannot “cure” Migraine but the headache could be significantly reduced or completely removed with proper treatment. It constitutes of prophylactic treatment and rescue treatment. A Prophylactic treatment is given on a daily basis in order to reduce “attacks” of Migraine.
Does chronic migraine ever go away?
For a lot of people chronic migraine develops gradually with migraine attacks becoming more frequent over time. Around 2.5 out of 100 people with episodic migraine will develop chronic migraine each year. For some people (around 2 out of 10) chronic migraine will go into remission within 2 years of becoming chronic.
What would cause constant migraines?
Mood disorders, especially anxiety and depression. Ongoing disrupted sleep pattern. Excessive caffeine intake. History of severe emotional (stressful life events) or physical trauma.
Why do I constantly have migraines?
Every person who has migraines has different triggers, but common ones include a lack of sleep, caffeine, and being under stress. Most people who get chronic migraines are women. This may be because hormone changes are another well-known cause.
Can you see migraines on MRI?
An MRI can’t diagnose migraines, cluster, or tension headaches, but it can help doctors rule out other medical conditions that may cause your symptoms, such as: A brain tumor. An infection in your brain, called an abscess. The buildup of fluid in the brain, called hydrocephalus.
What happens in brain during migraine?
One aspect of migraine pain theory explains that migraine pain happens due to waves of activity by groups of excitable brain cells. These trigger chemicals, such as serotonin, to narrow blood vessels. Serotonin is a chemical necessary for communication between nerve cells.
Can you get on disability for migraines?
The bottom line. If you’re unable to work due to chronic migraine, you can apply for disability benefits. You need to have enough work credits and evidence that you can’t work anymore due to your migraine symptoms. Migraine disability may be difficult to prove, but it can be done.
Are migraines mini strokes?
The kind of stroke that tends to be mistaken for a migraine is called a transient ischemic attack, or TIA. It’s also known as a “mini stroke” because blood flow to your brain is cut off only for a short time. Symptoms are less severe than with a regular stroke and may last less than an hour.
What’s in the migraine cocktail?
The exact medications used in a migraine cocktail can vary, but it typically includes triptans, NSAIDs, and antiemetics. A migraine cocktail is also available in OTC medication. OTC products usually contain aspirin, acetaminophen, and caffeine.
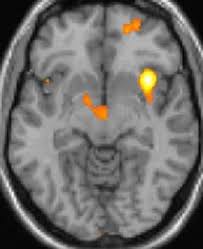
What does migraine look like on MRI?
In some migraine patients, an MRI may show white spots on the brain. These spots are called white matter hyperintensities (WMHs), which are lesions in the brain visualized by areas of increased brightness. They can vary in size and location in areas of the brain.
Are migraines and Alzheimer’s related?
Last year, Tyas led a study of 679 community-dwelling seniors in Manitoba, Canada, that showed people with a history of migraines were three times more likely to develop any type of dementia and more than four times as likely to develop Alzheimer’s disease.
What are the red flags for headaches?
“Red flags” for secondary disorders include sudden onset of headache, onset of headache after 50 years of age, increased frequency or severity of headache, new onset of headache with an underlying medical condition, headache with concomitant systemic illness, focal neurologic signs or symptoms, papilledema and headache
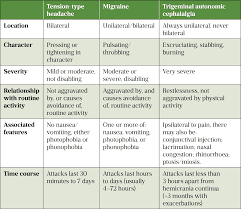
When is a migraine not a migraine?
migraine without aura – the most common type, where the migraine happens without the specific warning signs. migraine aura without headache, also known as silent migraine – where an aura or other migraine symptoms are experienced, but a headache does not develop.
Why does throwing up relieve migraines?
According to a 2013 review paper, vomiting may help with migraine headache symptoms, because it: changes blood flow to reduce pain or inflammation. releases chemicals that ease pain, such as endorphins. occurs toward the end of a migraine episode, leading to a reduction in symptoms.
Why does B2 help migraines?
In the body, vitamin B2 (riboflavin) participates in many metabolic processes. Specifically, this water-soluble vitamin may play a role in pathways involved in the development of migraine ( 5 ). For example, migraine episodes are thought to be associated with oxidative stress and brain inflammation.