Can migraines cause you to pass out? An aura also can occur without being followed by a headache. Rarely, migraines can cause unusual neurological symptoms such as dizziness, loss of vision, passing out, numbness, weakness or tingling.
When should you go to the ER for migraine? Go to the ER if you are experiencing severe migraine symptoms, or symptoms such as confusion, fever and vision changes, neck stiffness, trouble speaking or numbness or weakness, even if other symptoms of migraine are present (e.g. light sensitivity, nausea).
Can migraines cause dizziness and fainting? People with migraine may have issues with their sense of balance or vision. Feeling dizzy, lightheaded or unsteady can be a symptom of migraine. More specifically, attacks or episodes of dizziness or vertigo can be a sign of vestibular migraine.
What does a brain Tumour headache feel like? Every patient’s pain experience is unique, but headaches associated with brain tumors tend to be constant and are worse at night or in the early morning. They are often described as dull, “pressure-type” headaches, though some patients also experience sharp or “stabbing” pain.
Can migraines cause you to pass out? – Additional Questions
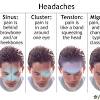
What are the 3 types of migraines?
The most common are migraine with aura (also known as a classic migraine) and migraine without aura (or common migraine). Other types include: Menstrual migraine.
When should I be worried about headaches and dizziness?
Generally, see your doctor if you experience any recurrent, sudden, severe, or prolonged and unexplained dizziness or vertigo. Get emergency medical care if you experience new, severe dizziness or vertigo along with any of the following: Sudden, severe headache.
How do you get rid of migraine dizziness?
How Are They Treated?
- Triptans. Take these migraine meds at the first sign of headache symptoms.
- Vestibular suppressant. It can ease your dizziness and motion sensitivity.
- If you have frequent or disabling vestibular migraines, your doctor may try drugs similar to traditional migraine prevention meds.
What neurological problems can cause dizziness?
The most common conditions are benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), vestibular migraine, Menière’s disease and vestibular neuritis/labyrinthitis.
Why do I need a brain scan for dizziness?
When patients present to the ED with dizziness, oftentimes the provider will order a computed tomography (CT) scan to rule out serious medical problems, such as intracranial bleeding or stroke.
What tests does a neurologist do for dizziness?
Testing such as MRI, CT scans and X-rays are often used to discover if additional medical conditions may be the cause of your dizziness.
Do brain tumors cause dizziness?
Brain tumors may cause weakness on one side of the body or face, clumsiness, dizziness, loss of balance, or stumbling.
What were your first signs of a brain tumor?
Symptoms
- New onset or change in pattern of headaches.
- Headaches that gradually become more frequent and more severe.
- Unexplained nausea or vomiting.
- Vision problems, such as blurred vision, double vision or loss of peripheral vision.
- Gradual loss of sensation or movement in an arm or a leg.
- Difficulty with balance.
What is usually the first symptom of a brain tumor?
Seizures. A tumor can irritate parts of the brain, leading to a seizure. Seizures are often the first signal of a brain tumor. In fact, about three out of every 10 people with a brain tumor were diagnosed after having a seizure.
Can an optician see a brain tumour?
Eye symptoms of a brain tumour
It is always worth seeing both your GP and an optometrist (optician) to investigate such symptoms. If your doctor suspects the presence of a brain tumour, they will immediately refer you for a scan at a hospital in order to be sure whether or not one is present.
Do eye floaters mean brain tumor?
Depending on the size and location of a tumor, abnormal eye movements and other vision changes like seeing floating spots or shapes knows as an “aura” may result. Behavioral or personality changes- A more subtle sign of a brain tumor can be a shift in a person’s behavior or personality.
How can you detect a brain tumor at home?
General symptoms include:
- Headaches, which may be severe and worsen with activity or in the early morning.
- Seizures. People may experience different types of seizures. Certain drugs can help prevent or control them.
- Personality or memory changes.
- Nausea or vomiting.
- Fatigue.
- Drowsiness.
- Sleep problems.
- Memory problems.
Can you survive a brain tumor?
As can be seen below, survival rates for some types of brain and spinal cord tumors can vary widely by age, with younger people tending to have better outlooks than older people.
Survival rates for more common adult brain and spinal cord tumors.
| Type of Tumor |
Glioblastoma |
| 5-Year Relative Survival Rate |
22% |
| 9% |
| 6% |
What are the chances I have a brain tumor?
Overall, the chance that a person will develop a malignant tumor of the brain or spinal cord in his or her lifetime is less than 1% (about 1 in 150 for men and 1 in 185 for women).
How do I know if my headache is a brain tumor?
Symptoms of a brain tumor headache
- headaches that wake you up at night.
- headache pain that changes as you change positions.
- headache pain that doesn’t respond to standard pain relievers such as aspirin, acetaminophen (Tylenol), or ibuprofen (Advil)
- headaches that last for days or weeks at a time.
How common are brain tumors by age?
Most primary CNS tumors in the 0- to 84-year age group were malignant (60%), and the overall incidence rate for malignant tumors for all ages was 5.64 per 100,000 person-years. The incidence rates for tumors of benign and uncertain behavior were 2.78 and 0.79 per 100,000 person-years, respectively.
Who is most likely to get a brain tumor?
Brain tumors are more common in children and older adults, although people of any age can develop a brain tumor. Gender. In general, men are more likely than women to develop a brain tumor. However, some specific types of brain tumors, such as meningioma, are more common in women.