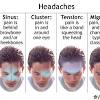
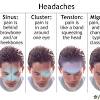
Can migraines cause a seizure? Migraine attacks may trigger a seizure.
This is considered a rare complication of a migraine with aura, which is also called a migraine aura-triggered seizure.
Can a migraine mimic a seizure? Some symptoms of migraine aura can look like a seizure, including vision problems, nausea, and uncontrolled movements. But during a seizure, you could be confused, feel depressed or fearful, or even lose consciousness. Seizures usually last 30 seconds to 2 minutes. Migraine aura, though, can last up to an hour.
What is Migralepsy? Migralepsy is defined as a seizure triggered by a migraine attack with aura: in particular, the seizure must fulfill the diagnostic criteria for a specific seizure, it has to occur in a patient suffering from migraine with aura (MA), during, or within 1 h of a migraine attack with aura (5).
Can migraines be mini seizures? A migraine-aura triggered seizure is defined as a seizure that occurs due to a migraine with aura and is not observed in migraines without aura. Experts suggest that migraine aura-induced seizures occur due to electrical changes in the brain that accompany an aura.
Can migraines cause a seizure? – Additional Questions
What does a seizure headache feel like?
These headaches are generally brief. They can be throbbing, steady, or sharp. Pre-ictal headaches are said to affect about 20% of people who have seizures that are difficult to control, but they may be under-reported because the seizure may interfere with memory of the headache.
Do migraines show on EEG?
In our study, according to headache types, there was a significantly high frequency of EEG abnormalities. Ten (24.4%) patients with migraines with aura had abnormal EEGs, and 12 (11.1%) patients with migraines without aura had abnormal EEGs (Figure 2).
Are migraines like small strokes?
Migraine can sometimes be mistaken for a stroke caused by bleeding on the brain, called a subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH), which is often characterised by a sudden, very severe headache. Unlike SAH, migraine headache is usually one-sided and throbbing, slow to come on and lasts for a shorter period of time.
What does an occipital seizure look like?
Seizures occurring in the occipital lobe are not common, but they affect your sight. Symptoms might include seeing patterns, flashing lights or colours, or images that appear to repeat before the eyes. There may be other visual effects as well, e.g. partial blindness may occur.
What are simple partial seizures?
A partial (focal) seizure happens when unusual electrical activity affects a small area of the brain. When the seizure does not affect awareness, it is known as a simple partial seizure. Simple partial seizures can be: Motor – affecting the muscles of the body. Sensory – affecting the senses.
What are non epileptic seizures?
PNES are attacks that may look like epileptic seizures but are not epileptic and instead are cause by psychological factors. Sometimes a specific traumatic event can be identified. PNES are sometimes referred to as psychogenic events, psychological events, or nonepileptic seizures (NES).
What can be mistaken for a seizure?
Movement disorders — Tics, tremors, and other involuntary movements can look like a myoclonic seizure or focal seizure, but they may be caused by things like Tourette’s syndrome, Parkinson’s disorder, Huntington’s disease, and other disorders that affect the brain.
Does an EEG show past seizures?
The EEG generally records brain waves between seizures, called interictal brain waves. These waves may or may not show evidence of seizure activity.
What are warning signs of a seizure?
General symptoms or warning signs of a seizure can include:
- Staring.
- Jerking movements of the arms and legs.
- Stiffening of the body.
- Loss of consciousness.
- Breathing problems or stopping breathing.
- Loss of bowel or bladder control.
- Falling suddenly for no apparent reason, especially when associated with loss of consciousness.
Can a doctor tell if you’ve had a seizure?
Electroencephalogram (EEG) – Using electrodes attached to your head, your doctors can measure the electrical activity in your brain. This helps to look for patterns to determine if and when another seizure might occur, and it can also help them rule out other possibilities.
What happens right before a seizure?
Seizure warning signs before the first ‘full-blown’ seizures
These warning signs may include feeling “funny” or dizzy, or having jerking and twitching for several years. Other signs include fainting, headaches, vomiting, losing sensation in a certain parts of the body, daydreaming, and blackouts.
What would cause a seizure all of a sudden?
Seizures can happen for many reasons; It may be from high levels of salt or sugar in your blood; brain injury from a stroke or head injury brain problems you are born with or perhaps a brain tumor. Dementia, such as Alzheimer’s disease, high fever or illnesses or infections that hurt your brain.
What are the 4 stages of a seizure?
Seizures take on many different forms and have a beginning (prodrome and aura), middle (ictal) and end (post-ictal) stage. These phases are described below.
What are the 3 most common causes of seizures in adults?
Overall, the most common etiology of adult onset seizures is stroke. Other causes in descending order are idiopathic seizures, CNS infections, metabolic causes, and brain tumors.
Can seizures damage brain?
Most types of seizures do not cause damage to the brain. However, having a prolonged, uncontrolled seizure can cause harm. Because of this, treat any seizure lasting over 5 minutes as a medical emergency.
Do seizures show up on MRI?
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy uses an MRI machine to analyze the molecular components of tissue in a particular area of the brain. This helps doctors differentiate a seizure from another condition, such as a metabolic disorder, tumor, or stroke.
How many seizures is too many?
A person is diagnosed with epilepsy when they have had two or more seizures. A seizure is a short change in normal brain activity. Seizures are the main sign of epilepsy.